
◆PL\Raman spectrum (standard function): PL\Raman spectrum excited by point-focusing or wide-field. ◆PL\Raman 2D Mapping (standard function): The laser is point-focusing on the sample, and the motorized stepping stages moves in two-dimensional space to realize the 2D Mapping function. ◆Motorized polarization-dependent spectrum and mapping (optional function): Polarization measurement can be realized by synchronous rotation of the polarizer and analyzer, or only rotation of the polarizer (analyzer).
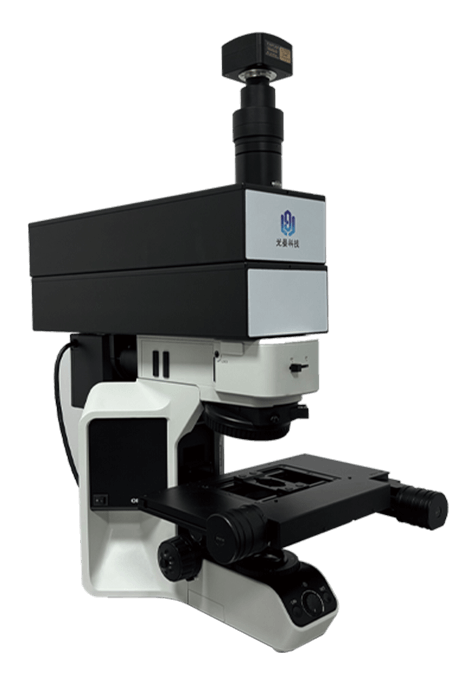
PL spectroscopy is mainly used for various types of luminescent materials, including semiconductor quantum dots, organic dye molecules, two-dimensional materials, perovskite films, etc., and is widely used in the fields of material chemistry, biomedicine, semiconductor physics and devices. Raman spectroscopy is mainly used to study the vibration spectra of various materials and molecules: Raman peak positions represent the chemical fingerprints of specific molecules, each Raman peak position corresponds to a specific molecular bond vibration, Raman shift reflects the material composition, Raman peak width reflects the crystal quality, Raman peak strength reflects the total amount of material, and Raman polarization reflects the crystal symmetry and orientation.
| Instrument | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Excitation light source | 450nm semiconductor laser with fiber-coupled output (laser wavelength can be customized). |
| Optical fiber spectrometer | slit 100 um, pixel 1 × 2048, dynamic range 3000:1, integration time 1ms~60s, wavelength range 300~1000nm or 900~1700nm (some parameters can be customized). |
| 2D motorized translation stages | minimum step size 0.05um, unidirectional repetition accuracy < 1um, travel 80mm*60mm. |
| Microscopic imaging module | imaging spatial resolution ≤ 1um; CMOS parameters: 1 inch, 2.4um pixels, resolution 15fps@5440 *3648; Half compound achromatic bright-field objective group: 5X-100X, 0.15-0.9NA; White-light Kohler illumination mode. |
| Laser incidence module | the resolution of incident light with point-focusing is 1um@0.9NA Objective; The range of wide-field excitation is 100um @0.9NA Objective; Point-focusing and wide-field excitation can be switched quickly, and multiple channels can be used for coupling incident laser; The angle repetition accuracy of the electric rotating motor is 0.1 degree/step, the angle range is 360 degrees, and the optical aperture is 20mm (polarization module is optional). |
| Confocal collection module | spatial resolution of confocal collection 1um@100X Objective @100um optical fiber core; Wave number resolution~10 cm-1 (depending on the resolution of spectrometer and optical system); The angle repetition accuracy of the electric rotating motor is 0.1 degree/step, the angle range is 360 degrees, and the optical aperture is 20mm (polarization module is optional); It is equipped with filter mounting base and corresponding band filter that can be pulled and switched. |